Variables, Expression and statements¶
Variables and Object References¶
Value and type¶
A value is one of the basic things a program works with, like a letter or a number.
The values we have seen so far are 1, 2, and 'Hello, World!'.
These values belong to different types: 2 is an integer (Integers), and 'Hello, World!' is a string (Strings),
so-called because it contains a “string” of letters. You (and the interpreter) can identify
strings because they are enclosed in quotation marks. We speak speak also of data type.
If you are not sure what type a value has, the interpreter can tell you.
>>> type('Hello, World!')
<class 'str'>
>>> type(17)
<class 'int'>
Not surprisingly, strings belong to the type str and integers belong to the type int.
Less obviously, numbers with a decimal point belong to a type called float,
because these numbers are represented in a format called floating point (Floating Point types).
>>> type(3.2)
<class 'float'>
What about values like '17' and '3.2'?
They look like numbers, but they are in quotation marks like strings.
>>> type('17')
<class 'str'>
>>> type('3.2')
<class 'str'>
They’re strings.
When you type a large integer, you might be tempted to use commas or space
between groups of three digits, as in 1,000,000.
This is not a legal integer in Python, but it is legal:
>>> 1,000,000
(1, 0, 0)
Well, that’s not what we expected at all! Python interprets 1,000,000
as a comma-separated sequence of integers.
This is the first example of a semantic error: the code
runs without producing an error message, but it doesn’t do the right thing.
In Python, both str and int are immutable. That is once set their value cannot be changed anymore.
there exist some datatype which are mutable (we will see what this difference implies between this to kind
of datatype in Mutable objects and Immutable objects and some examples of mutable and immutable
data types in Data Types and Collection Data Types)
To convert a data item from one type to another, we can use the syntax datatype(item). For example:
>>> int("45")
45
>>> str(45)
'45'
The int conversion is tolerant of leading and trailing whitespace. So int(” 45 “) would have worked just as well.
The str conversion can be applied to almost data item.
If a conversion fails, an exception is raised (we will see fully Exception Handling later).
>>> int('Hello World!')
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
ValueError: invalid literal for int() with base 10: 'Hello World!'
Variables and Object references¶
Once we have data item (or values), the next thing we need is variables in which to store them.
A variable is a name that refers to a value.
One of the most powerful features of a programming language is the ability to manipulate variables.
As I mentioned earlier, in Python everything is an object, even int or string.
>>> isinstance(3, object)
True
>>> isinstance('blue', object)
True
Note
An object is “something” which pack together
- a state, for instance the value 3 for the int or ‘blue’ for the string.
- and a behavior: a set of methods (the operations that we can do on this object).
For instance ‘blue’ is the state, upper is a method applied to the value ‘blue’:
>>> 'blue'.upper() 'BLUE'
The object oriented programming is out of the scope of this course. So we don’t see more about the objects.
So Python does not have variable as such, but instead has object references. When it comes to immutable objects
like str or int, there is no discernable difference between variable and an object reference.
As for mutable objects there is a difference, but it rarely maters in practice. So we will use the terms of variable
or object reference interchangeably.
Let’s look at few examples and see what’s happend in details:
x = 3
color = 'green'
y = color
The syntax is simply object reference = value. There is no need of predeclaration
and no need to specify the value’s type. When Python execute
- the first statement it creates a
intobject with the value3and create the object reference callxthat refer to the int object. For all practical purpose we saythat variable x has been assigned the "3" integer. - The second statement is similar.
- The third creates a new object reference y and sets it to refer to the same object that the color reference object refers to (in this case the str object containing the value “green”).
Let’s see what python do behind the scene:
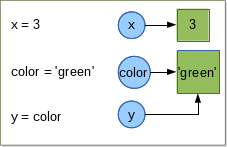
= operator is not the same as the variable assignment operator in some other languages.= operator binds an object in memory to an object reference. If the object reference already exists
it simply re-bound to refer to the object on the right of = operator; if the reference does not exist, it simply created by the = operator.
Let us continue with the previous example and do some rebinding.

>>> print x, color, y #in python3 syntax or print_function import >>> print(x, color, y)
3 green green
>>> x = y
>>> print x, color, y
green green green
Note
comments begin with a # and continue until the end of the line
3 Python is free to garbage it.Python uses dynamic typing, which means that an object reference can be rebound to refer to a different object (which may be a different data type) at any time.

Immutable objects¶
As I mentioned in previous paragraph immutable objects are objects that we cannot change the state (the value). We can rebind the reference which was refer to an immutable object to a new object with an other value, but we cannot change the value of the object itself. We already seen immutable objects, int, str. There is a lot of other data types which are immutable we will see them in details in Data Types and Collection Data Types .
Mutable objects¶
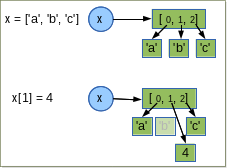
By contrast to the immutable objects, the mutable object are object that we can modify the state (the value).
One example of immutable object is the list (we will see the Lists in details in chapter about Collection Data Types).
A list is an object to hold a collection of data items. In the list the items are ordered.
We can easily insert, remove, items whenever we want.
Under the hood, the lists do not store data items at all, but rather object references. When lists are created and when items are inserted, they take copies of the object references they are given.

Variable name and keywords¶
Programmers generally choose names for their variables that are meaningful, they document what the variable is used for.
Variable names (also calls identifiers) non empty sequence of characters that can be arbitrarily long. This sequence consists of a “start character” and a “non zero” or more “continuation characters”. Such an identifier must obey a couple of rules and ideally follow some conventions.
The first rule concern the start and continuation characters.
- start character can be any letter or the underscore.
- The continuation character can be any character that is permit as a start character, or pretty well any non white space character including digit.
The underscore character,
"_"is often used in names with multiple words such asscoring_matrix.Identifiers are case sensitive, so far GENESEQUENCE, GeneSequence, Genesequence or genesequence are different identifiers.
Note
In Python3 the default encoding is utf8. So letter can be anything that Unicode considers to be a letter, as non english letters.
Note
The precise set of characters that are permitted are describe in the Python documentation (), and in PEP3131
- The identifier cannot have the same name a one of the Python’s keywords.
Python 2 has 31 keywords:
| and | del | global | not | while |
| as | elif | if | or | with |
| assert | else | import | pass | yield |
| break | except | in | ||
| class | finally | is | raise | |
| continue | for | lambda | return | |
| def | from | nonlocal | try |
Note
In Python 2, nonlocal does not exists, but exec is a keyword.
The first convention is: Don’t use the names of any of Python’s predefined identifiers for you own identifiers. So, avoid using NotImplemented or Ellipsis and the name of any of Python’s built-in data types (such as int, float, str, list, tuple), and any of Python’s built-in functions or exceptions.
The second convention concern the uses of underscore
_. Names that begin and end with two underscores as__eq__should not used. Python defines various special methods and variables that use such names. In the case of special methods, we can reimplement them, that is, make our own version of them (we will not cover this topic during this course), but not to introduce new names. A single underscore can be used as an identifier, and inside an interactive interpreter or Python Shell, _ holds the results of the last expression that was evaluated. In normal program _ does not exists unles we use it explicitly. Some developers like to use _ when they don’t intend to use it, for instance in loops when they don’t care about the items being looped over, or when they unpack a sequence and don’t care of some value:for _ in (0,1,2,3,4,5): print("Hello") a , _, b, _ = (1,2,3,4)
If you give a variable an illegal name, you get a syntax error:
>>> 76trombones = 'big parade'
SyntaxError: invalid syntax
>>> more@ = 1000000
SyntaxError: invalid syntax
>>> class = 'Advanced Theoretical Zymurgy'
SyntaxError: invalid syntax
76trombonesis illegal because it does not begin with a letter.more@is illegal because it contains an illegal character,@.classis one of Python’s keywords.
Note
All these naming conventions are details in Follow the conventions (Python Enhancement Proposal), Style Guide for Python Code. The pep8 gives coding conventions for the Python code. These guidelines are intended to improve the readability of code and make it consistent across the wide spectrum of Python code. Consistency with this style guide is important. Consistency within a project is more important. Most of the time when you start a project you start it alone, it’s your project you can choose the style you want. But one day your code will be read by an other, for helping you to debug, because you want to start a collaboration, a student get back your code to continue the project, because you want to publish your code. It will be very much easier to understand what you did if you follow these conventions.
Summary¶
In this chapter we learned that a value have a data type. Python have different data types, some of them are immutable the others are mutable. We also create object reference to handle data item. A variable or reference object can handle different data type at any time, this is called the dynamic typing.